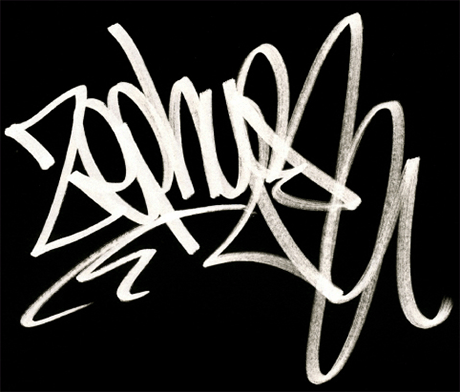computer misuse act (1990)
- Illegal access to computer material aka cracking
- Illegal access and modification of any computer material
- Illegal access with intent to carry out malicious activity
This act helps protect peoples computers from being corrupted by another person or being personally attacked while on their computer by another individual. Protect yourself from being influenced by evils of the society who do the same mis-usage of computer technology.
This act was introduced to deter more serious criminals from using a computer to assist them.
A disadvantage of the computer misuse act is that it has been see by enforcement agencies to be ineffective to repel offenders from breaking this act and has been notices by some others to be potentially problematic from a net neutrality standpoint.
copyright, design and patents act (1988)
The Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, is the current UK copyright law. It gives the creators of literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works the right to control the ways in which their material may be used. The rights cover: Broadcast and public performance, copying, adapting, issuing, renting and lending copies to the public. In many cases, the creator will also have the right to be identified as the author and to object to distortions of his work.
Copyright arises when an individual or organisation creates a work, and applies to a work if it is regarded as original, and exhibits a degree of labour, skill or judgement.
Interpretation is related to the independent creation rather than the idea behind the creation. For example, your idea for a book would not itself be protected, but the actual content of a book you write would be. In other words, someone else is still entitled to write their own book around the same idea, provided they do not directly copy or adapt yours to do so.
Names, titles, short phrases and colours are not generally considered unique or substantial enough to be covered, but a creation, such as a logo, that combines these elements may be.
Normally the individual or collective who authored the work will exclusively own the rights. However, if a work is produced as part of employment then normally the work belongs to the person/company who hired the individual. For freelance or commissioned work, rights will usually belong to the author of the work, unless there is an agreement to the contrary, (i.e. in a contract for service).
Only the owner, or his exclusive licensee can bring proceedings in the courts against an infringement.
Advantages of the copyright, design and patents act
- No one can copy your ideas
- Cant steal your artwork, music, designs
- Ensures any idea you have patented isn't stolen
disadvantages of the copyright, design and patents act
- You have to pay to patent ideas
- The punishment for breaking the act isquite intense at up to 2 years in prison
 Downloaded items:
Downloaded items:
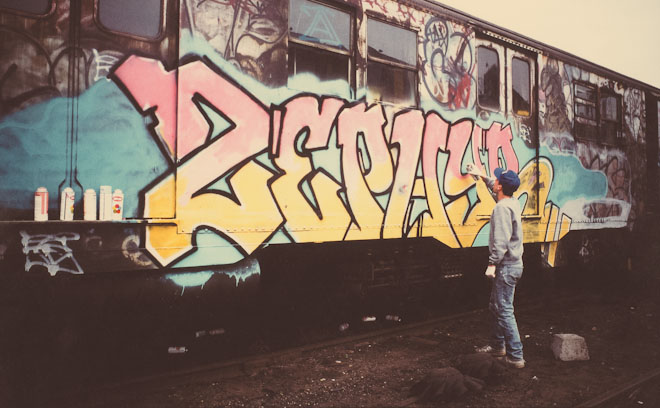




















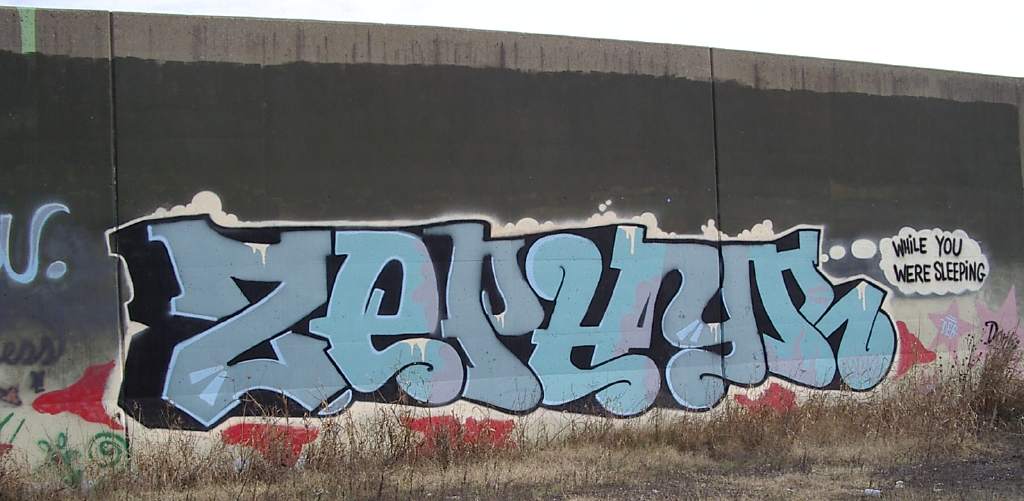
 Born Andrew Witten, Zephyr began his art career in 1977, painting his Zephyr moniker in subways and on random walls. He was part of the first wave of graffiti artists to make the transition to galleries, collectors, and commercial work. He is one of the pioneers in graffiti art and his style is considered as one of the standard graffiti designs.
Born Andrew Witten, Zephyr began his art career in 1977, painting his Zephyr moniker in subways and on random walls. He was part of the first wave of graffiti artists to make the transition to galleries, collectors, and commercial work. He is one of the pioneers in graffiti art and his style is considered as one of the standard graffiti designs.